30天学会streamlit
st.write
st.slider
st.slider 能够显示一个滑条输入组件。
支持一下几种数据类型:int、float、date、time 和 datetime。
我们要做什么?
我们今天要搭建一个简单的应用,来展示如何使用滑条组件接收各类来自用户的输入。
应用的流程:
- 用户通过调整滑条来选择数值
- 将用户所选数值显示出来
st.selectbox
st.multiselect
st.checkbox
latex
代码
import streamlit as st
st.header('st.latex')
st.latex(r'''
a + ar + a r^2 + a r^3 + \cdots + a r^{n-1} =
\sum_{k=0}^{n-1} ar^k =
a \left(\frac{1-r^{n}}{1-r}\right)
''')
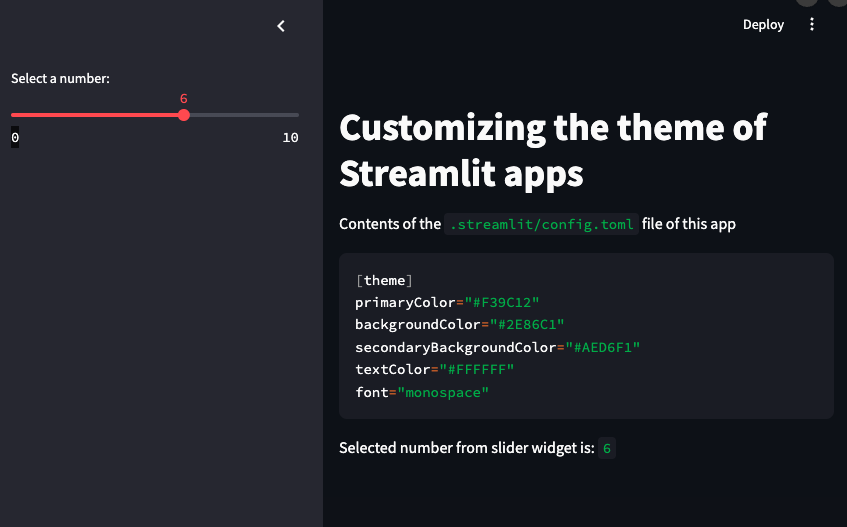
自定义 Streamlit 应用的主题
代码
以下是 streamlit_app.py 文件中的内容:
import streamlit as st
st.title('Customizing the theme of Streamlit apps')
st.write('Contents of the `.streamlit/config.toml` file of this app')
st.code("""
[theme]
primaryColor="#F39C12"
backgroundColor="#2E86C1"
secondaryBackgroundColor="#AED6F1"
textColor="#FFFFFF"
font="monospace"
""")
number = st.sidebar.slider('Select a number:', 0, 10, 5)
st.write('Selected number from slider widget is:', number)
以下是 .streamlit/config.toml 配置文件中的内容:
[theme]
primaryColor="#F39C12"
backgroundColor="#2E86C1"
secondaryBackgroundColor="#AED6F1"
textColor="#FFFFFF"
font="monospace"
显示效果
st.secrets
代码
import streamlit as st
st.title('st.secrets')
st.write(st.secrets['message'])
效果展示
没学会,展示略过
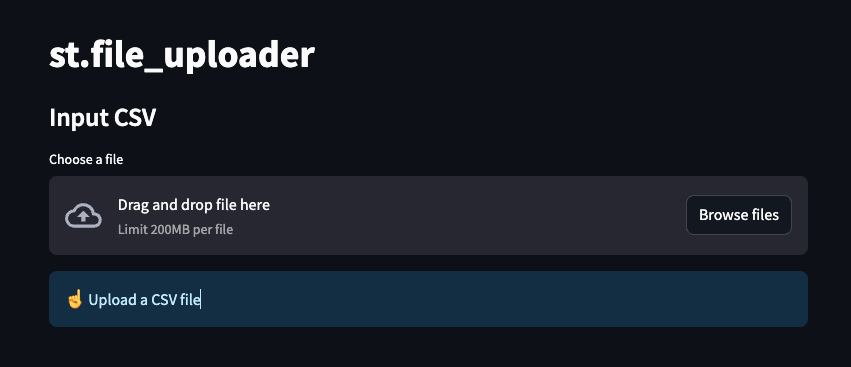
st.file_uploader
代码
import streamlit as st
import pandas as pd
st.title('st.file_uploader')
st.subheader('Input CSV')
uploaded_file = st.file_uploader("Choose a file")
if uploaded_file is not None:
df = pd.read_csv(uploaded_file)
st.subheader('DataFrame')
st.write(df)
st.subheader('Descriptive Statistics')
st.write(df.describe())
else:
st.info('☝️ Upload a CSV file')
效果展示
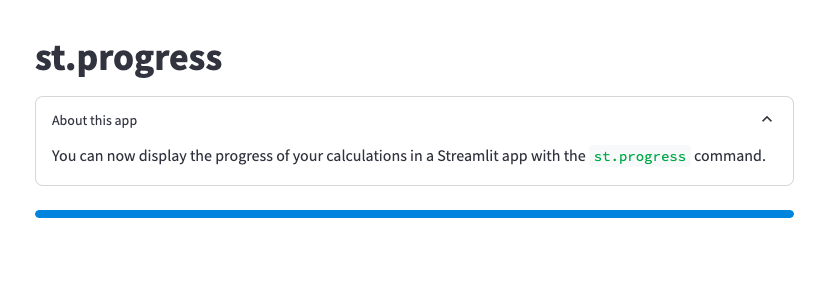
st.progress
代码
import streamlit as st
import time
st.title('st.progress')
with st.expander('About this app'):
st.write('You can now display the progress of your calculations in a Streamlit app with the `st.progress` command.')
my_bar = st.progress(0)
for percent_complete in range(100):
time.sleep(0.05)
my_bar.progress(percent_complete + 1)
st.balloons()
效果
st.form
st.form 创建一个将内容组合起来的表单,并且带有一个 "Submit" 提交按钮。
通常情况下,当用户与组件交互的时候,Streamlit 应用就会重新运行一遍。
表单是是一个视觉上将元素和组件编组的容器,并且应当包含一个提交按钮。在此之中,用户可以与一个或多个组件进行任意次交互都不会触发重新运行。直到最后提交按钮被按下时,所有表单内组件的数值会一次性更新并传给 Streamlit。
你可以使用 with 语句来向表单对象添加内容(推荐),或者也可以将其作为一个对象直接调用其对象方法(即首先将表单组件存入一个变量,随后调用该变量的 Streamlit 方法)。可见样例应用。
表单有一些限制:
- 所有表单都应当包含一个
st.form_submit_button对象 st.button和st.download_button将无法在表单中使用- 表单能够出现在你应用的任何地方(包括侧边栏、列等等),唯独不能嵌入另一个表单之中
import streamlit as st
st.title('st.form')
# Full example of using the with notation
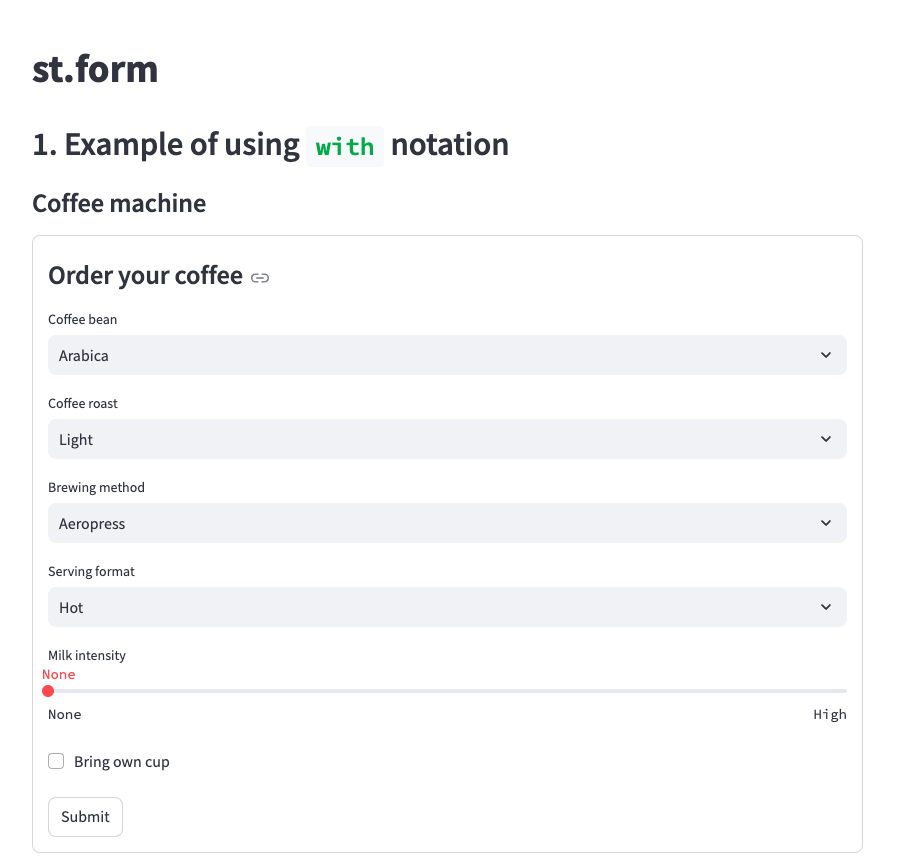
st.header('1. Example of using `with` notation')
st.subheader('Coffee machine')
with st.form('my_form'):
st.subheader('**Order your coffee**')
# Input widgets
coffee_bean_val = st.selectbox('Coffee bean', ['Arabica', 'Robusta'])
coffee_roast_val = st.selectbox('Coffee roast', ['Light', 'Medium', 'Dark'])
brewing_val = st.selectbox('Brewing method', ['Aeropress', 'Drip', 'French press', 'Moka pot', 'Siphon'])
serving_type_val = st.selectbox('Serving format', ['Hot', 'Iced', 'Frappe'])
milk_val = st.select_slider('Milk intensity', ['None', 'Low', 'Medium', 'High'])
owncup_val = st.checkbox('Bring own cup')
# Every form must have a submit button
submitted = st.form_submit_button('Submit')
if submitted:
st.markdown(f'''
☕ You have ordered:
- Coffee bean: `{coffee_bean_val}`
- Coffee roast: `{coffee_roast_val}`
- Brewing: `{brewing_val}`
- Serving type: `{serving_type_val}`
- Milk: `{milk_val}`
- Bring own cup: `{owncup_val}`
''')
else:
st.write('☝️ Place your order!')
# Short example of using an object notation
st.header('2. Example of object notation')
form = st.form('my_form_2')
selected_val = form.slider('Select a value')
form.form_submit_button('Submit')
st.write('Selected value: ', selected_val)
展示效果
st.experimental_get_query_params
st.experimental_get_query_params 允许获取用户所用链接中的查询参数。
st.cache
st.cache 使得你可以优化 Streamlit 应用的性能。
Streamlit 提供了一个缓存机制,使你的应用即便是在从互联网加载数据、操作大数据集或者进行大开销的计算时仍可以保持高性能。这主要通过 @st.cache 装饰器来实现。
当你用 @st.cache 装饰器标记一个函数时,它将告诉 Streamlit 在该函数执行前需要做如下一些检查:
- 函数的输入参数是否发生了变化
- 函数中使用的外部变量是否发生了变化
- 函数的主体是否发生了变化
- 函数中用到的所有函数的主体是否发生了变化
如果以上任意一项不满足,即 Streamlit 第一次见到这四者的这种顺序组合时,它将会执行这个函数,并且将结果存储于本地缓存中。然后当下一次该带缓存的函数被调用时,如果以上四项均未发生改变,则 Streamlit 会直接跳过函数执行,而直接从缓存中调用先前的结果并返回。
Streamlit 通过哈希散列来追踪这些条件的变化。你可以把缓存当成一种存储在内存之中的键值对结构,其中上述四项总和的哈希值为键,以函数实际返回的引用为值。
最后,@st.cache 支持一些参数来配置缓存的行为。详见我们的 API 参考。
代码
import streamlit as st
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
from time import time
st.title('st.cache')
# Using cache
a0 = time()
st.subheader('Using st.cache')
@st.cache(suppress_st_warning=True)
def load_data_a():
df = pd.DataFrame(
np.random.rand(2000000, 5),
columns=['a', 'b', 'c', 'd', 'e']
)
return df
st.write(load_data_a())
a1 = time()
st.info(a1-a0)
# Not using cache
b0 = time()
st.subheader('Not using st.cache')
def load_data_b():
df = pd.DataFrame(
np.random.rand(2000000, 5),
columns=['a', 'b', 'c', 'd', 'e']
)
return df
st.write(load_data_b())
b1 = time()
st.info(b1-b0)
st.session_state
我们将通过一个浏览器标签页访问 Streamlit 应用定义为一个会话(Session)。每个连接至 Streamlit 服务器的标签页都将创建一个会话。每当你与应用中组件交互时,Streamlit 将从上到下地重新运行整个应用。每次重新运行都将会清空历史:没有变量将被保留下来。
而会话状态(Session State)是一个在同一会话的不同次重新运行间共享变量的方法。除了能够存储和保留状态,Streamlit 还提供了使用回调函数更改状态的支持。
在此教程中,我们将构建一个重量换算应用,并描述会话状态以及回调函数的用法。
st.session_state 将允许我们在 Streamlit 应用中使用会话状态。
代码
import streamlit as st
st.title('st.session_state')
def lbs_to_kg():
st.session_state.kg = st.session_state.lbs/2.2046
def kg_to_lbs():
st.session_state.lbs = st.session_state.kg*2.2046
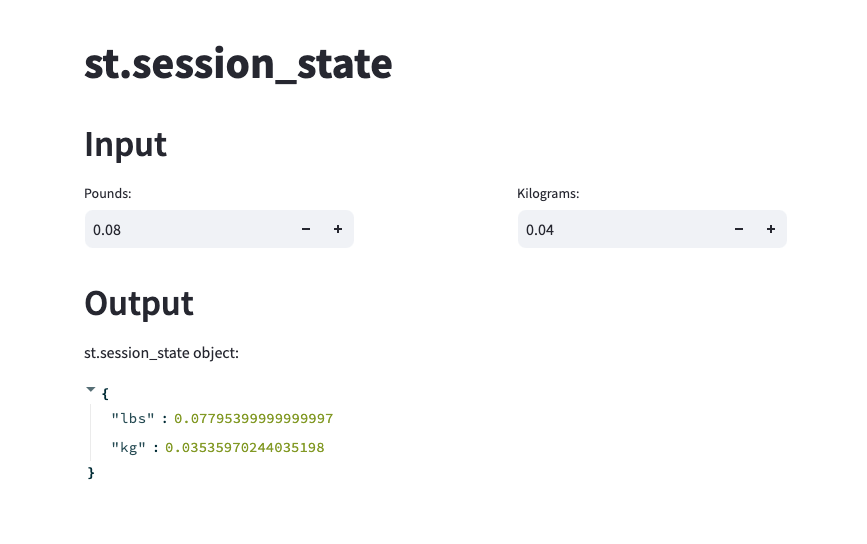
st.header('Input')
col1, spacer, col2 = st.columns([2,1,2])
with col1:
pounds = st.number_input("Pounds:", key = "lbs", on_change = lbs_to_kg)
with col2:
kilogram = st.number_input("Kilograms:", key = "kg", on_change = kg_to_lbs)
st.header('Output')
st.write("st.session_state object:", st.session_state)
效果展示
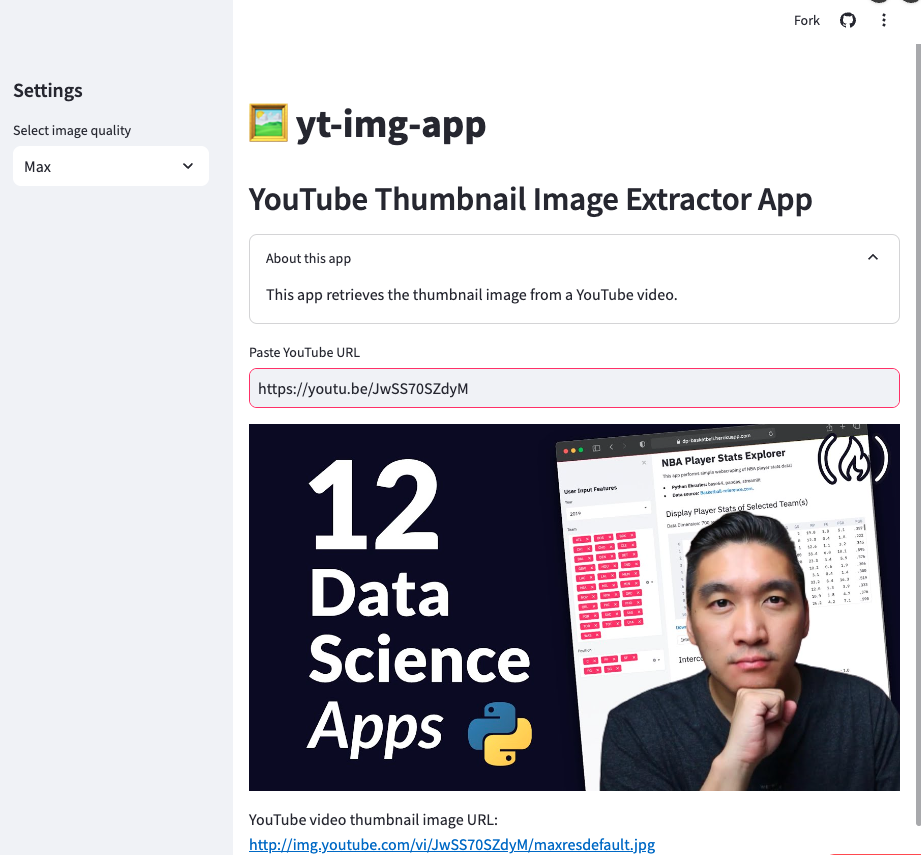
创建 Streamlit 应用之艺术
代码
import streamlit as st
st.title('🖼️ yt-img-app')
st.header('YouTube Thumbnail Image Extractor App')
with st.expander('About this app'):
st.write('This app retrieves the thumbnail image from a YouTube video.')
# Image settings
st.sidebar.header('Settings')
img_dict = {'Max': 'maxresdefault', 'High': 'hqdefault', 'Medium': 'mqdefault', 'Standard': 'sddefault'}
selected_img_quality = st.sidebar.selectbox('Select image quality', ['Max', 'High', 'Medium', 'Standard'])
img_quality = img_dict[selected_img_quality]
yt_url = st.text_input('Paste YouTube URL', 'https://youtu.be/JwSS70SZdyM')
def get_ytid(input_url):
if 'youtu.be' in input_url:
ytid = input_url.split('/')[-1]
if 'youtube.com' in input_url:
ytid = input_url.split('=')[-1]
return ytid
# Display YouTube thumbnail image
if yt_url != '':
ytid = get_ytid(yt_url) # yt or yt_url
yt_img = f'http://img.youtube.com/vi/{ytid}/{img_quality}.jpg'
st.image(yt_img)
st.write('YouTube video thumbnail image URL: ', yt_img)
else:
st.write('☝️ Enter URL to continue ...')
效果展示